Metals
Properties of Metals
| Physical | Chemical |
|---|---|
| High density | Form basic oxides |
| Shiny when polished | Form positive ions |
| Malleable | |
| Ductile | |
| High m.p. And b.p. | |
| Conductor of heat & electricity |
Alloys
An alloy is two or more metals, or a metal and non-metal which have been made molten and then mixed together
Alloys are used because they have improved qualities for a particular job over the pure metals
| Alloy | Made from | Special Properties | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Copper and zinc | Stronger and more resistant to corrosion | Electrical fittings, car radiators |
| Bronze | Copper and tin | Harder, stronger and sonorous | Statues, springs, coins |
| Stainless steel | Iron, chromium and nickel | Does not rust | Kitchen sinks, cutlery, chemical plant |
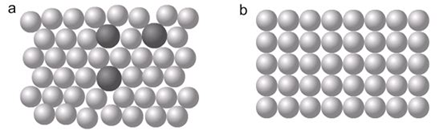
Metals are often used as alloys because they have an increased range of uses and mixture of atoms gives an irregular structure which stops layers sliding over each other easily; they are stronger
This is what the structure of an alloy (a) looks like, compared to a pure metal (b).
Reactivity Series
K - Potassium Na - Sodium Ca – Calcium Mg – Magnesium Al – Aluminium C – Carbon Zn – Zinc Fe – Iron Pb – Lead H – Hydrogen Cu – Copper Ag – Silver Au – Gold | This places metals in order of their readiness to take part in |
Everything above hydrogen can displace hydrogen from | |
Metals above carbon, their oxides cannot be reduced by carbon. | |
More reactive metals will react with cold water, and less | |
Aluminium seems unreactive because it forms an oxide layer |
Displacement Reactions
These are reactions in which metals compete for oxygen or anions
The more reactive metal will displace the less reactive metal from oxygen or an anion.
If more reactive metal has oxygen or an anion, no reaction occurs
The bigger the difference in reactivity between the two metals, the faster the reaction
Thermal Decomposition
| Group | Metal Carbonate | Metal Hydroxide | Metal Nitrate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group I (except lithium) | Do not decompose | Do not decompose | Metal nitrite and oxygen |
| Group II, lithium & transition metals | Metal oxide and carbon dioxide | Metal oxide and water | Metal oxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen |
Extraction of Metals
Ores more difficult to decompose from gold to potassium
More powerful/expensive method of extraction from gold to potassium
Metal | Extraction Method |
|---|---|
K - Potassium Na - Sodium Ca – Calcium Mg – Magnesium Al – Aluminum | Reduction via electrolysis |
Carbon | |
Zn – Zinc Fe – Iron Pb – Lead | Reducing via heating with Carbon or Carbon Monoxide |
Hydrogen | |
Cu – Copper Ag – Silver Au – Gold | Occur naturally |
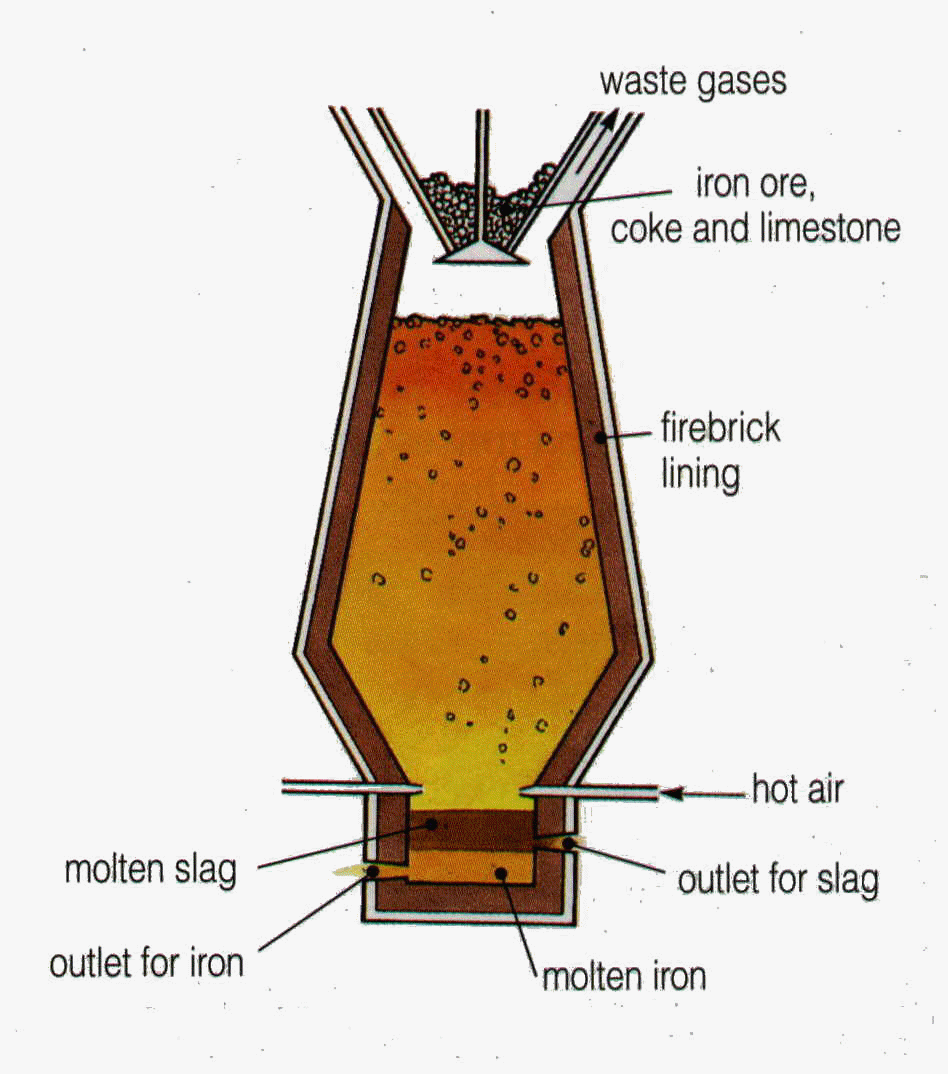
Extracting Iron
Ore = hematite (Fe~2~O~3~)
Uses of slag
To make roads
To make cement
Coke burns with air
carbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide reacts with coke
carbon dioxide + carbon →
carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide reduces Iron(III) oxide to iron
iron(III) oxide + carbon monoxide → iron + carbon dioxide
The limestone reacts with impurities to form slag
calcium carbonate + silicon dioxide → calcium silicate + carbon dioxide
Iron to Steel
Molten iron from blast furnace is poured into an oxygen furnace.
Calcium oxide is added, and a jet of oxygen is turned on.
The calcium oxide neutralizes acidic impurities, forming slag that is skimmed off and oxygen burns the other impurities away.
The carbon content is checked continually until it is just right then the oxygen is turned off.
Mild Steel (0.25% carbon) -- Used in machinery and car bodies
Medium carbon steel (0.5%) -- Used in railway lines
High carbon steel (1.5% carbon) -- Used in knives and blades
Extracting Zinc
Ore = Zinc Blende = Zinc Sulphide (ZnS)
Zinc blende is roasted in air to convert it to zinc oxide
Zinc oxide is reduced using coke to zinc and carbon monoxide in the furnace
As zinc is volatile, the gaseous metal is distilled leaving less-volatile impurities behind.
Zinc is condensed and liquid is run into mould.
Uses of Metal
Aluminum
Airplane/Cars (Strong/Low density/resistant to corrosion)
Cans/Foil (Resistant to corrosion/malleable)
Overhead cable (Good conductor of electricity/ductile)
Zinc
Galvanizes Iron = coats it to stop it rusting
Alloys -- brass/bronze
Batteries
Sacrificial Protection
Copper
Electrical Wiring (Good conductor of electricity/Ductile)
Cooking utensils (Malleable/good conductor of heat)
Roofs (hard wearing against weather