Organic Chemistry
Fuels
Fuels to know:
Coal
Natural gas: main constituent is methane
Petroleum: a mixture of hydrocarbons which can be separated into fractions
Uses of Petroleum Fractions
Refinery gas: bottled gas for heating and cooking
Gasoline fraction: fuel (petrol) in cars
Naphtha fraction: making chemicals
Kerosene/paraffin fraction: jet fuel, lamps
Diesel oil/gas oil fraction: fuel in diesel engines
Fuel oil fraction: fuel in ships and home heating systems
Lubricating fraction: lubricants, waxes and polishes
Bitumen: making roads
Name of Compounds
Name ending → compound-type name
"ane" → alkane
"ene" → alkene
"ol" → alcohol
"oic acid" → carboxylic acid
"yl", "oate" → ester
Alkanes
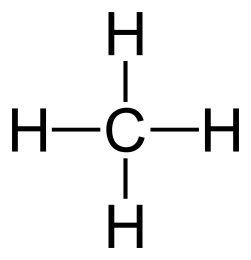
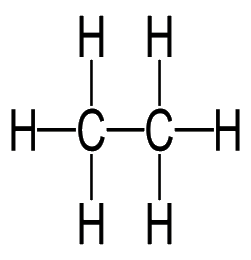
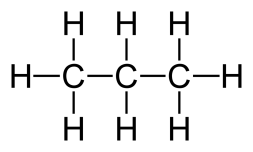
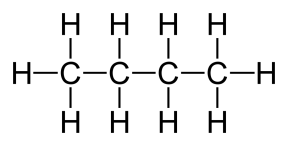
General formula = C~n~H~2n+2~
| Methane (n=1) | Ethane (n=2) |
|---|---|
 |  |
| Propane (n=3) | Butane (n=4) |
 |  |
- Each carbon atoms in an alkene has four covalent single bonds -- this makes them quite unreactive.
Combustion:
Complete combustion: enough oxygen supply so water and carbon dioxide form.
e.g. CH~4~ + 2O~2~ → CO~2~ + 2H~2~O
Incomplete: is not enough oxygen to burn them cleanly so either carbon monoxide and water or carbon and water form.
e.g. 2CH~4~ + 3O~2~ → 2CO + 4H~2~O or
e.g. CH~4~ + O~2~ → C + 2H~2~O
Chlorine substitution:
Sunlight or light is necessary
A chlorine atom replaces a hydrogen atom
This can happen to all hydrogen atoms if there is enough chlorine.
e.g. CH~4~ + Cl~2~ → (light) → HCl + CH~3~Cl / CH~2~Cl~2~ / CHCl~3~ / CCl~4~
Compounds = chloromethane / di/tri/tetrachloromethane
Alkenes
General formula = C~n~H~2n~
Functional group: C=C bond
| (n=1) | Ethene (n=2) |
|---|---|
| N/A | 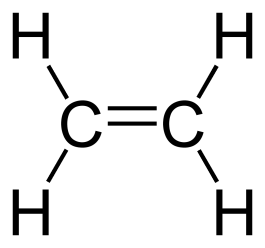 |
| Propene (n=3) | But-1-ene (n=4) |
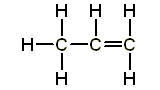 | 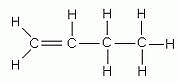 |
Cracking:
Thermal decomposition reaction, in which an alkene (and sometimes hydrogen) are produced from an alkane.
Cracking always produces short chain compound with a C=C bond
e.g. Cracking of ethane will give ethene and hydrogen
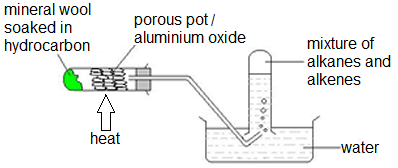
- Butane → Ethane + Ethene ; C~4~H~10~ → C~2~H~6~ + C~2~H~4~
| Saturated Hydrocarbons | Unsaturated Hydrocarbons |
|---|---|
| Have NO double bonds | Have double bonds |
| Do not react with aqueous bromine, so the mixture stays orange. | React with aqueous bromine, turning the mixture from orange to colourless. |
Addition Polymerisation
A polymer is a compound with very long carbon chains made up of monomer units.
Poly(ethene) / Polythene: is a polymer produced from ethene by addition polymerization
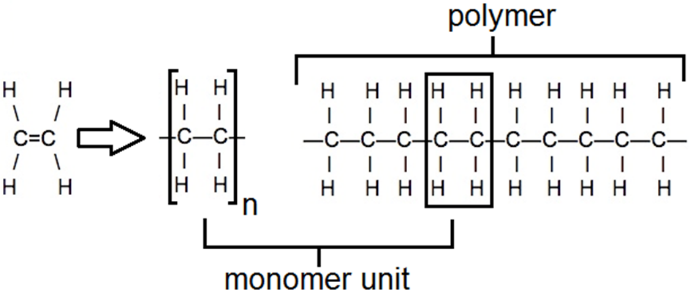
Double bond splits and polymer is formed
Alkenes' Addition Reactions
With bromine: (the test for saturation)
e.g. ethene (g) + bromine (aq) → 1,2-dibromomethane (l)
With steam: forms alcohols with heat, pressure and a catalyst
e.g. ethene (g) + steam (g) ⇌ ethanol (l)
With hydrogen: double bond breaks down to for an alkane with heat, pressure and a catalyst
e.g. ethene (g) + hydrogen (g) → ethane (g)
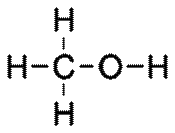
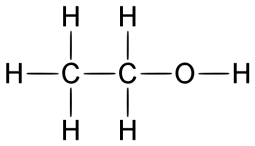
Alcohols
General formula = C~n~H~2n+1~OH
Functional group: OH
| Methanol (n=1) | Ethanol (n=2) |
|---|---|
 |  |
| Propanol (n=3) | Butanol (n=4) |
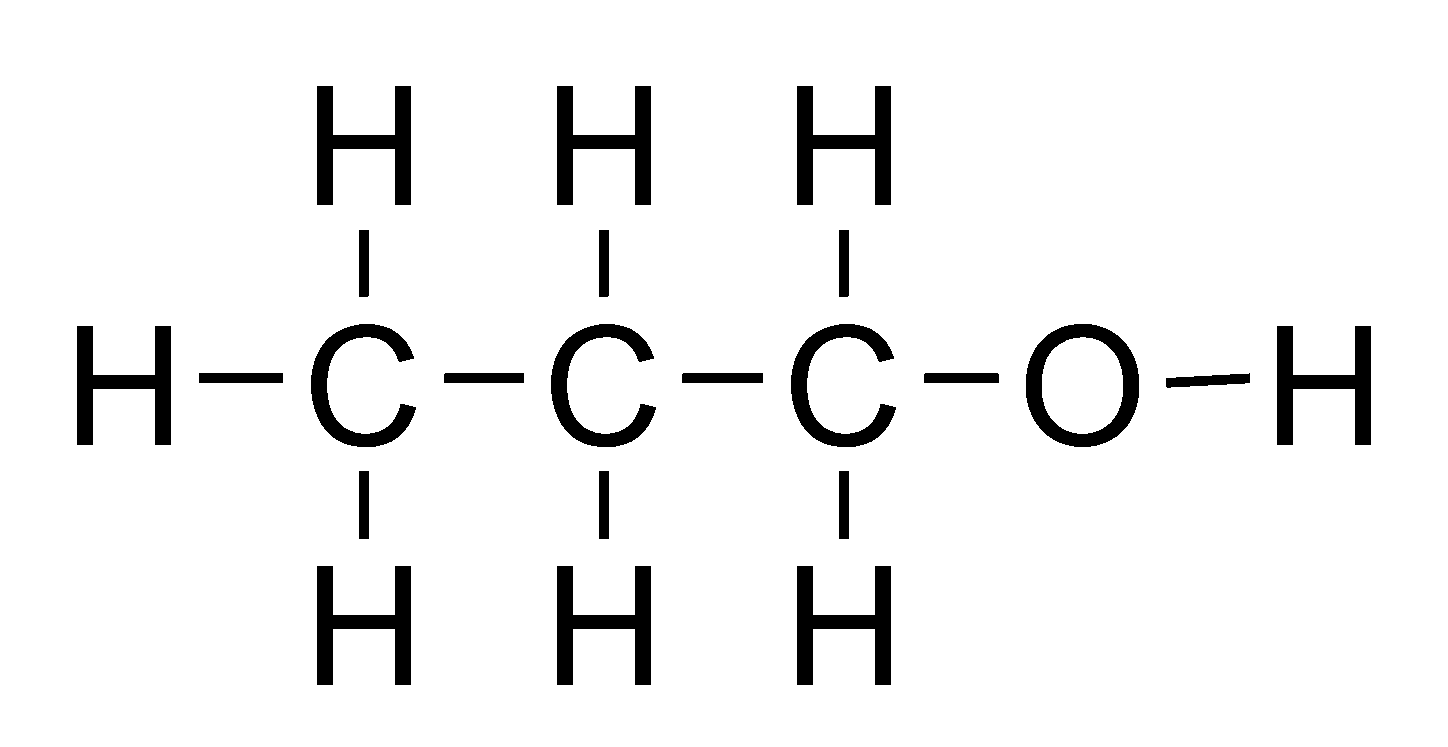 | 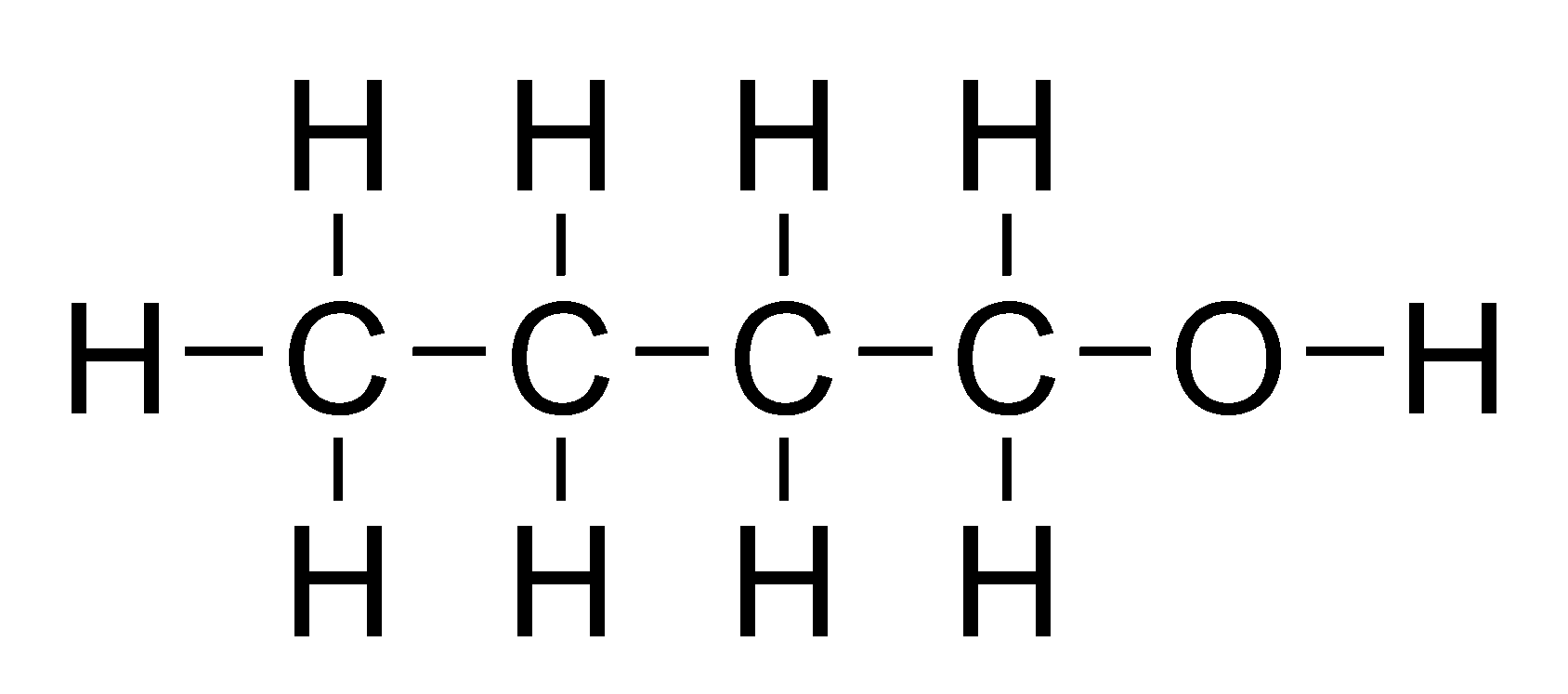 |
Formed by:
| Fermentation | Catalytic Addition of Steam to Ethene |
|---|---|
| Enzymes in yeast break down glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide, giving out heat | Ethene is obtained by cracking long-chain alkenes from oil. |
| Can be done with substances that contain cellulose, starch or glucose |
The ethene reacts with steam (reversibly) in the following conditions:
570°C
60-70atm
Catalyst = phosphoric acid
| | Done by grinding source (e.g. grapes) and adding enzymes to break down cellulose and starch into glucose. | Low temperature gives a better yield, but high temperature is used to give a better rate of reaction. | | Leave it to ferment. | | | Fractional distillation is used to get ethanol from the mixture | |
Fermentation:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Renewable source | Lots of material needed so big tanks needed |
| Good use of waste organic material | Fractional distillation is expensive |
| Slow process | |
| Batch process |
From Ethene:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Fast | Oil is a non-renewable resource |
| Continuous process | Lot of energy to make steam and get right conditions |
| Pure ethanol | Lot of ethene is un-reacted, (and then recycled) |
| Smaller containers |
Ethanol burns well in oxygen, giving out plenty of heat, as well as carbon dioxide and water.
Ethanol is used as a:
Solvent: to dissolve things than water cannot. Evaporates easily, so used as solvent in glues, printing inks & perfumes
Fuel: added to or instead of petrol, because it burns cleanly
Carboxylic Acids
General formula = C~n~H~2n+1~COOH
Functional group: COOH
| Methanoic Acid (n=1) | Ethanoic Acid (n=2) |
|---|---|
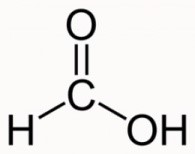 | 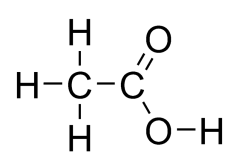 |
| Propanoic Acid (n=3) | Butanoic acid (n=4) |
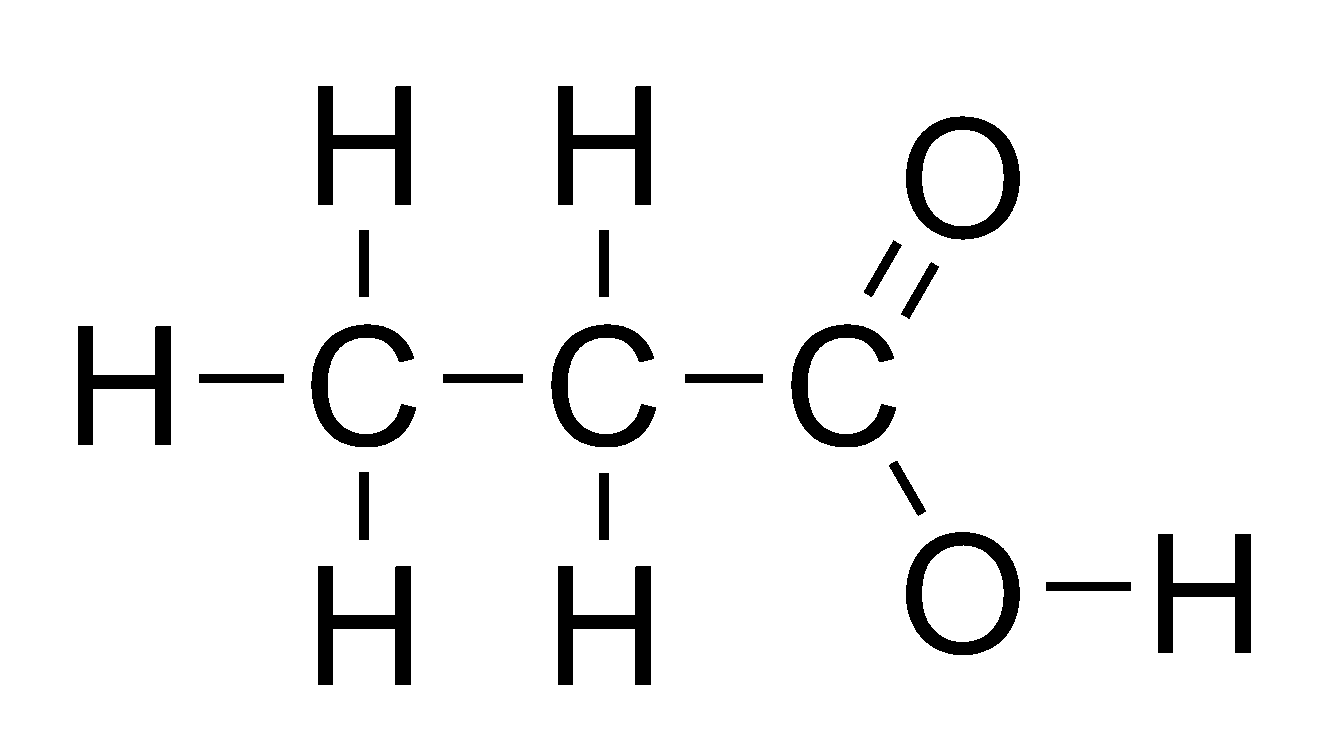 | 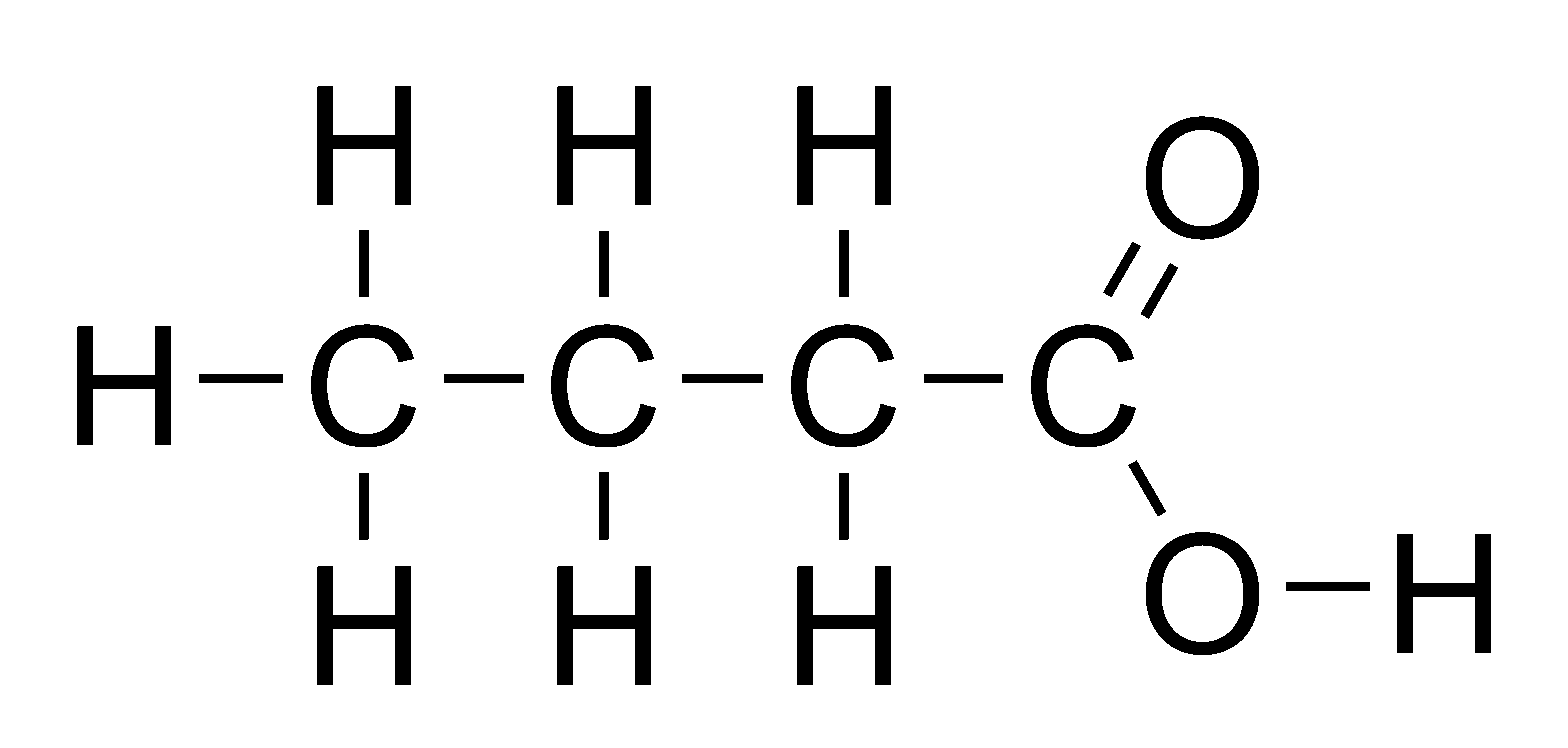 |
Properties of Ethanoic Acid:
Weak acid with high pH and low dissociation
Formed by:
Oxidation of ethanol
With acidified potassium mangenate (VII)
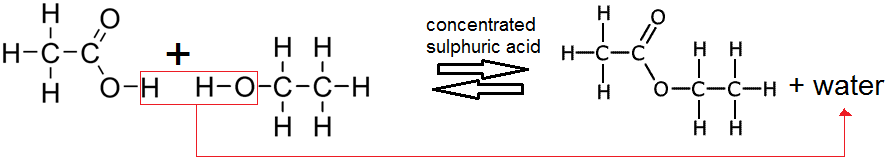
Carboxylic acids react with alcohols to give esters, in a condensation reaction, for example:
Ethanoic acid + ethanol ⇌ ethyl ethanoate + water (alcohol = -yl & carboxylic acid = -oate)
Macromolecules
- Large molecules built up from small units (monomers).
Different macromolecules have different units and/or different linkages
Example of:
Small units (monomers) Linkages Macromolecules Glucose Amide Protein Amino acids Ester Starch Fatty acids and glycerol Lipids
| Use | Structure | |
|---|---|---|
| Polythene | Plastic bags and gloves, clingfilm (low density), mugs, bowls, chairs, dustbins (high density) |  |
| Polychloroethane (PVC) | Water pipes, wellingtons, hoses, covering for electricity cables |  |
| Polypropene | Crates, ropes | 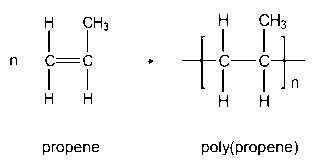 |
| Polystyrene | Used as expanded polystyrene in fast-food cartons, packaging, and insulation for roofs and walls |  |
| Teflon | Coated on frying pans to make them non-stick, fabric protector, windscreen wipers, flooring |  |
Making nylon:
- Uses: ropes, fishing nets and lines, tents, curtains
- Monomers are:
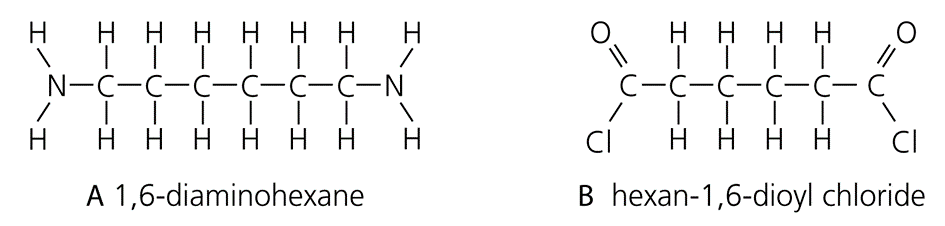
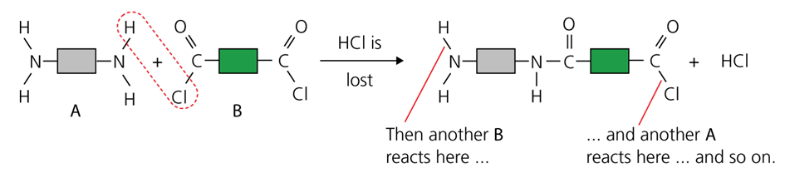
No double bonds break, instead single bonds break, and new single bonds form.
The monomers are able to join to each other by eliminating a small molecule: hydrogen chloride.
This reaction continues at each the two monomers.
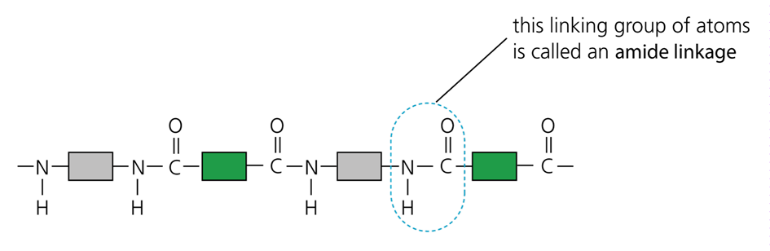
Thousands of molecules join together, giving a macromolecule:
Making terylene
Uses: clothing (especially mixed with cotton), thread
Monomers are:
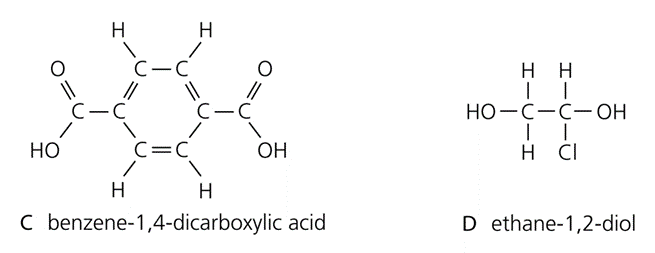
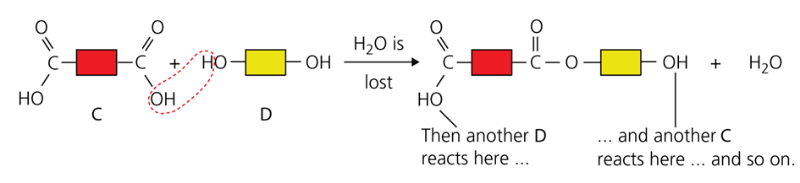
- The monomers join by eliminating a water molecule. Thousands of molecules join up, giving a macromolecule
Pollution from Plastics
Choke birds, fish and other animals that try to eat them. Or they fill up the animals' stomachs so that they can't eat proper food, and starve to death.
They clog up drains and sewers and cause flooding.
They collect in rivers, and get in the way of fish. Some river beds now contain a thick layer of plastic
They blow into trees and onto beaches. So the place looks a mess. Tourists become put off.
Natural Macromolecules
- Food's main constituents are proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Proteins:
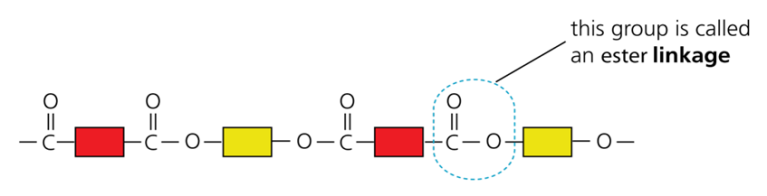
- Proteins contain the same linkages (amide links) as nylon, but with different units. Their structure is:
- In digestion proteins are broken down into amino acids (hydrolysis).
Fats:
Fats are esters possessing the same linkage as Terylene (ester links) but with different units.
Soap is a product of the hydrolysis of fat. It is done using sodium hydroxide (as opposed to acid, in digestion). The hydrolysis gives glycerol and the sodium salts of fatty acids. The salts are used as soaps.
Carbohydrates:
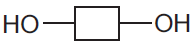
- Complex carbohydrates: are a large number of joined sugar units (monosaccharide like glucose). The sugar units are represented like this:
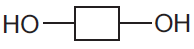
They join together in a condensation polymerization
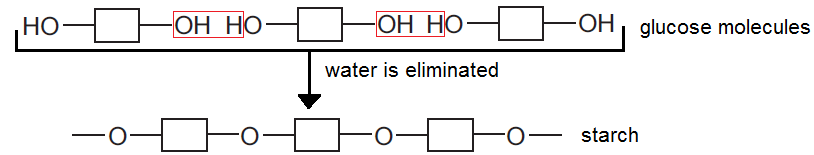
In digestion, the hydrolysis (Decomposition of a chemical compound by reaction with water) of starch happens in the mouth by the enzyme amylase to make glucose
Hydrolysis:
Starch → glucose
Proteins → amino acids
Fats → fatty acids and glycerol
But if hydrolysis is not complete, macromolecules are not completely broken down so you get a mixture of molecules of different sizes
Identification:
Chromatography can be used to identify products & substances
However, amino acids and sugars are colourless when dissolved in water, so a locating agent is used.
Substances can be identified using Rf values or by matching them with spots which are horizontal