Atoms, Elements and Compounds
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
| Particle | Relative charge | Mass (atomic mass) |
|---|---|---|
| Proton | +1 | 1 |
| Neutron | 0 | 1 |
| Electron | -1 |
Proton number: number of protons in an atom (and number of electrons in an atom)
Nucleon number: number of protons + neutrons in an atom.
Isotopes: atoms of same element with different no. of neutrons
- E.g. Carbon 12 and Carbon 14.
- Two types: non-radioactive isotopes and radioactive-isotopes which are unstable atoms that break down giving radiations
- Medical use: cancer treatment (radiotherapy) -- rays kill cancer cells using cobalt-60
- Industrial use: to check for leaks -- radioisotopes (tracers) added to oil/gas. At leaks radiation is detected using a Geiger counter.
In the periodic table
- The proton number increases by 1 when you go to the right
- When you go one element down, you increase proton number by 8 in the first 3 periods (transition elements not included)
Electrons are arranged in electron shells.
Atoms want to have full outer shells (full set of valency electrons), this is why they react.
Noble gases have full outer shells so they have no need to react.
Electron shell structure: 2, 8, 8, 18.
More reactive elements have a greater desire to have a full outer shell, so also form more stable compounds.
Bonding: the Structure of Matter
Element: substance that cannot be split into anything simpler, in a chemical reaction. Each element has a unique proton number.
Mixture: two or more elements mixed together but not chemically combined
Compound: substance in which two or more different elements are chemically combined
| Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|
| Strong | Brittle |
| Good conductors of heat & electricity | Poor conductors of heat & electricity (except graphite) |
| High m.p. and b.p. | Lower m.p. and b.p. than metals |
| High density | Low density |
| Forms basic oxides | Forms acidic oxides |
| Forms cations in reactions | Forms anions in reactions |
| Malleable and ductile | |
| Sonorous | |
| Some are magnetic |
Alloy: Mixture of two or more metals or mixture of one or more metal with a non-metal, to improve its properties
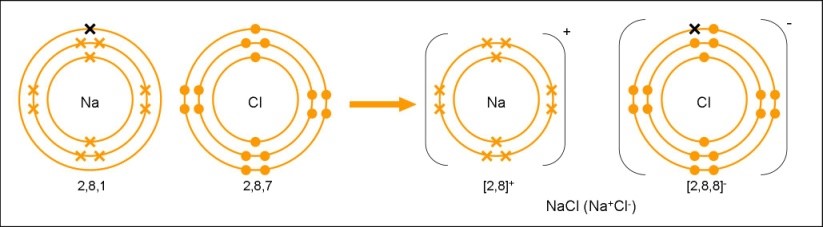
Ions and Ionic Bonds
Chemical bond formed by transfer of s from one atom to another
Metals lose s to form cations, non-metals gain s to form anions
Positive cations & negative anions attract to each other
Strong electrostatic force of attraction between positive cations and negative anions is called ionic bonding
| Property | Reason |
|---|---|
| Form giant lattice | Cations and anions attract |
| High m.p. and b.p. | Strong bonds between ions |
| Don't conduct electricity when solid | Ions can't move |
| Conduct electricity when molten/aqueous | Ions can move |
| Usually soluble in water | Not required |
Molecules and Covalent Bonds
When atoms share s to obtain a noble gas electron structure.
Covalent bonding takes place between non-metals only.
| Single Bond | Double Bond | Triple Bond |
|---|---|---|
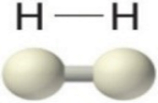 | 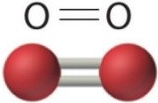 | 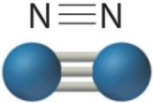 |
| 2ē shared | 4ēs shared | 6ēs shared |
| Property | Reason |
|---|---|
| Low m.p. and b.p. | Weak intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules |
| Usually liquid, gas or low m.p solid | No mobile ions/electrons |
| Don't conduct electricity | Not required |
| Usually insoluble in water |
Example:

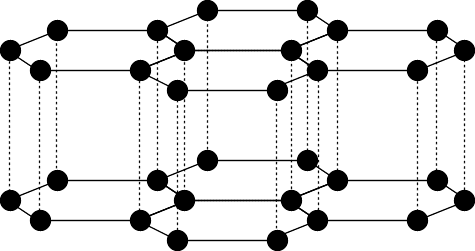
Macromolecules
| Diamond | Graphite | Silicon Dioxide |
|---|---|---|
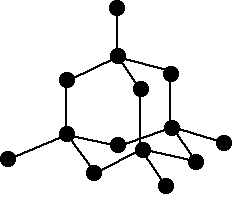 |  | 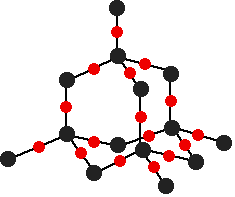 |
| Four bonds | Three bonds | Makes up sand |
| High m.p. | Made of flat sheets | Each Si is bonded to 4 oxygen atoms, and each oxygen is bonded to 2 silicon atoms |
| Doesn't conduct | Held together by weak forces so is soft ∴ used as a lubricant | ∴ it has a high m.p. and is hard, like diamond |
| Used for cutting as is srongest known substance | Conducts electricity as it has one free e- |
Melting point: high - structure made up of strong covalent bonds.
Electrical: don’t conduct electricity - have no mobile ions or electrons, except for graphite.
Strength: hard - exists in tetrahedral structure but graphite is soft.
Metallic Bonding
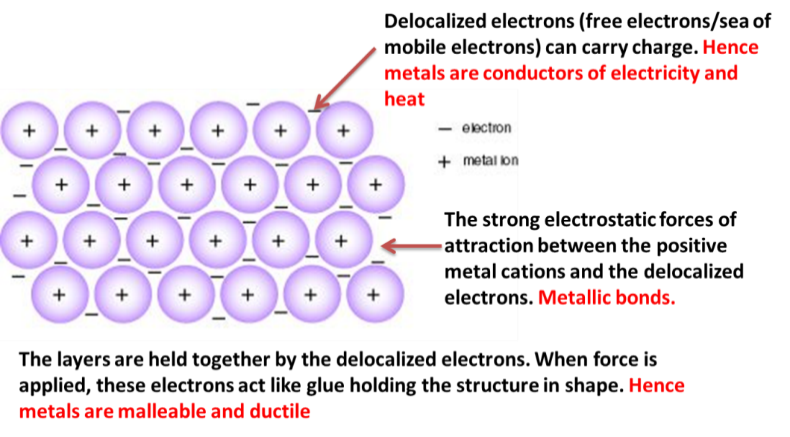
Positive ions held together by electrons -- acts like glue