Acids, Bases and Salts
Properties of Acids
An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions (H^+^) and are described as proton donors (H^+^)
Acids turn blue litmus indicator paper (or solution) red.
Have pH 1 to 6
Acid + metal → salt + hydrogen gas
Acid + base → salt + water
Acid + metal carbonate → salt + carbon dioxide + water
Strong acids completely ionize in water producing lots of H^+^ ions
Weak acids partially ionize in water producing few H^+^ ions
Properties of Bases
Bases are insoluble substances which neutralize acids to form a salt and water only and are proton acceptors
Alkalis turn red litmus indicator paper (or solution) to blue.
Have pH 8 to 14.
Base + acid → salt + water (+ CO~2~ when base is a metal carbonate)
Base + ammonium salt → salt + ammonia gas + water
Strong alkalis completely ionize in water producing lots of OH^-^ ions
Weak alkalis partially ionize in water producing OH^-^ ions
Neutral
Neutral substances are pH 7.
Acidity in soil:
Plants grow at a pH near 7.
If it is too acidic or alkaline they will not grow.
Acidic soil is fixed by adding lime.
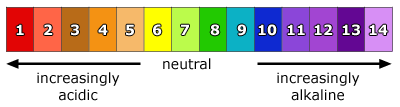
- pH is the concentration of H^+^ ions per dm^3^ of solution
Indicators
| Indicator | Color in acid | Color in alkaline |
|---|---|---|
| Phenolphthalein | Colorless | Pink |
| Methyl orange | Pink | Yellow |
| Methyl red | Red | Yellow |
| Red litmus | Red | Blue |
| Blue litmus | Red | Blue |
Types of Oxides
Metal oxides are basic e.g. iron oxide and magnesium oxide
Non-metal oxides are acidic e.g. sulphur oxide and carbon dioxide
Aluminum, zinc and lead form amphoteric oxides e.g. zinc oxide
Oxides which are neither acidic or basic are neutral e.g. water and carbon monoxide
Preparation of Salts
A salt is a substance formed when all the replaceable hydrogen ions of an acid are replaced by metal ions or the ammonium ion
- Salts can either be soluble or insoluble
| Soluble Salts | Insoluble Salts |
|---|---|
| All sodium, potassium and ammonium salts | |
| All nitrates | |
| Chlorides | Except silver and lead |
| Sulphates | Except barium, lead and calcium |
| Potassium, sodium and ammonium carbonates | All other carbonates |
Type of Salts
| Type of Salt Required | Acid used |
|---|---|
| Sulphate | Sulphuric acid |
| Nitrate | Nitric acid |
| Chloride | Hydrochloric acid |
| Ethanoate | Ethanoic acid |
Starting with a Metal
Add excess metal to an acid
When bubbling (hydrogen) stops the reaction is done
Filter off excess metal
Starting with an Insoluble Base
Add insoluble base to acid and heat gently, it will dissolve
Keep adding until no more dissolves (reaction is done)
Filter out the insoluble (excess) base
Starting with an Alkali (Titration)
Put a certain amount alkali in a flask
Add phenolphthalein
Add acid from a burette, stirring, until it goes colorless
Find out how much acid you used
Repeat, to be more accurate
Evaporate water from neutral solution
Test for Aqueous Cations
| Cation | Effect of AQ. NaOH | Effect of AQ. Ammonia |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al^3+^) | White soluble precipitate formed giving a colorless solution | White precipitate formed |
| Ammonium (NH~4~^+^) | Ammonium gas produced turns damp red litmus blue | |
| Calcium (Ca^2+^) | White precipitate formed | No precipitate/ slight white precipitate |
| Copper (Cu^2+^) | Light blue precipitate formed | Light blue soluble precipitate formed giving dark blue solution |
| Iron(II) (Fe^2+^) | Green precipitate formed | Green precipitate formed |
| Iron(III) (Fe^3+^) | Red-brown precipitate formed | Red-brown precipitate formed |
| Zinc (Zn^2+^) | White soluble precipitate formed giving a colorless solution | White soluble precipitate formed giving a colorless solution |
Test for Anions
| Anion | Test | Test result |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonate (CO~3~^2-^) | Add dilute nitric acid | Bubble gas through limewater--from colorless to cloudy |
| Chloride (Cl^-^) | Add nitric acid, then aqueous silver nitrate | White precipitated formed |
| Bromide (Br^-^) | Add nitric acid, then aq. silver nitrate | Cream precipitate formed |
| Iodide (I^-^) | Add nitric acid, then aqueous silver nitrate | Bright yellow precipitate formed |
| Nitrate (NO~3~^-^) | Add aqueous sodium hydroxide then add aluminium | Gas produced turns damp red litmus paper blue |
| Sulphate (SO~4~^2-^) | Add dilute nitric acid, then add aq. barium nitrate | White precipitate formed |
Test for Gases
| Gas | Test and test result |
|---|---|
| Ammonia (NH~3~) | Damp red litmus paper turns blue |
| Carbon dioxide (CO~2~) | Bubble gas through--from colorless to cloudy |
| Chlorine (Cl~2~) | Bleaches red/blue litmus paper |
| Hydrogen (H~2~) | Place lighted splint, squeaky pop |
| Oxygen (O~2~) | Place glowing splint, splint relights |