Chemical Energetics
Energetics of a Reaction
Exothermic reaction: one that releases heat energy into the surrounding
Endothermic reaction: one which absorbs heat energy from the surroundings
Bond breaking is endothermic
Bond making is exothermic
| Exothermic reaction | Endothermic reaction |
|---|---|
| Energy given out to the surroundings | Energy is taken in from the surroundings |
| Surroundings become hot | Surroundings become cold |
| Bond making -- exothermic | Bond breaking -- endothermic |
Energy Level Diagrams
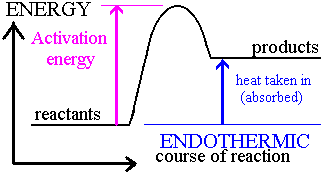
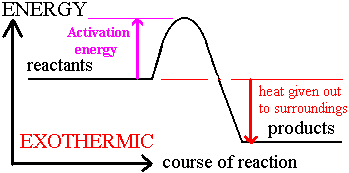
Bond Energy
- This is the amount of energy consumed or liberated when a bond is broken or formed in kJ/mol
ΔH=Bond Breaking+Bond FormingΔH=BondBreaking+BondForming
If overall heat energy is negative, reaction is exothermic
If overall heat energy is positive, reaction is endothermic
Production of Energy
A fuel is a substance which can be conveniently used as a source of energy.
Burning fuels (like oil) to form oxides is an exothermic reaction.
The heat from burning fuels is used in power plants to create steam from water and turn turbines.
In order for any material to combust three things must be present:
Fuel
Heat
Oxygen
A good fuel would:
Be cheap
Be available in large quantities
Ba a liquid at room temperature
Produce a large amount of energy when combusted
Not produce polluting gases
Hydrogen
Burns explosively with oxygen, so it is used in rockets.
In a fuel cell, it combines with oxygen without burning.
Produced by reacting methane gas with steam
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Produces a lot of energy | Difficult to transport as it is a gas at room temperature |
| Abundant on earth (sea) | Forms explosive mixture with air -- very dangerous |
| Less pollutant | |
| Renewable fuel |
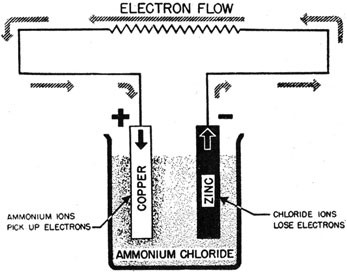
Simple Cells
A cell is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy and is composed of two metals of different reactivity connected by an external circuit and an electrolyte
The process works due to the different reactivity of metals
Consists of a negative pole (the more reactive metal) and a positive pole (less reactive metal) and an electrolyte.
The greater the difference in reactivity of the two metals, the greater the voltage will be.
The electrons flow because one metal is more reactive, so it has a stronger drive to give up its electrons.
The atoms give up electrons and enter the solution as ions.
Radioactive Isotopes
Uranium-235 can be used in nuclear power stations to produce electricity
The radioactive isotope is bombarded by neutrons resulting in a lot of heat being produced
Small amount of radioactive fuel produces large amount of heat
Advantages: lots of energy is from a small amount and no CO~2~
Disadvantage: radioactive waste produced and non-renewable