Experimental Techniques
Measurement
| Variable | Apparatus |
|---|---|
| Time | Stopwatch or Clock |
| Temperature | Thermomemeter (liquid in glass, thermistor or thermocouple) |
| Mass | Balance |
Measuring Volume:
 |  |  |  |  |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beaker | Burette | Pippette | Measuring Cylinder | Gas Syringe |
Critertia of Purity
Paper chromatography:
- Drop substance to center of filter paper and allow it to dry
- Drop water on substance, one drop at a time
- Paper + rings = chromatogram.
- Principle: Difference in solubility separates different pigments
- Substances travel across paper at different rates which is why they separate into rings
- Method works because different substances travel at different levels of attraction to it
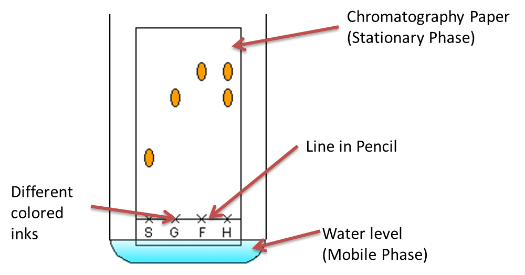
Stationary phase is material on which separation takes place
Mobile phase consists of the mixture you want to separate, dissolved in a solvent.
Interpreting simple chromatograms:
- Number of rings/dots = number of substances
- If two dots travel the same distance up the paper they are the same substance.
- You can calculate the Rf value to identify a substance, given by the formula:
To make colourless substances visible, use a locating agent:
- Dry paper in oven
- Spray it with locating agent
- Heat it for 10 minutes in oven
Assesing purity from m.p./b.p:
- Pure substances have a definite, sharp m.p./b.p.
- Substance+impurity has lower m.p. and higher b.p.
- More impurity means bigger change
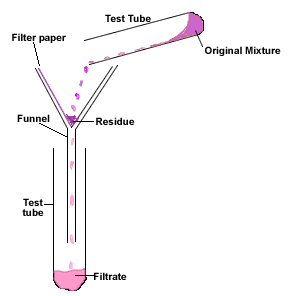
Filtration
Mixture goes in a funnel with filter paper, into a flask.
Residue is insoluble and stays at top.
Filtrate goes through.
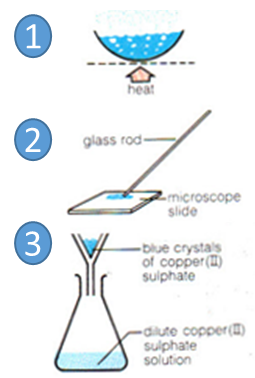
Crystallization
Some water in the solution is evaporated so solution becomes more concentrated.
A drop is placed on a slide to check if crystals are forming.
Solution is left to cool and crystallise.
Crystals are filtered to remove solvent.
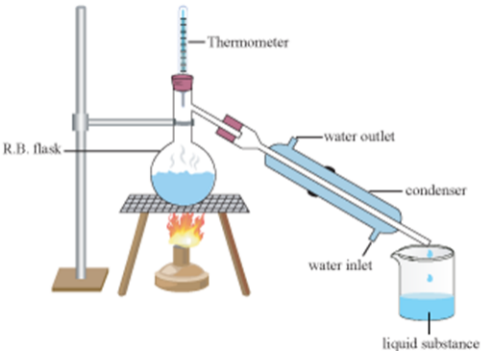
Simple Distillation
Impure liquid is heated
It boils, and steam rises into the condenser
Impurities are left behind
Condenser is cold so steam condenses to the pure liquid and it drops into the beaker
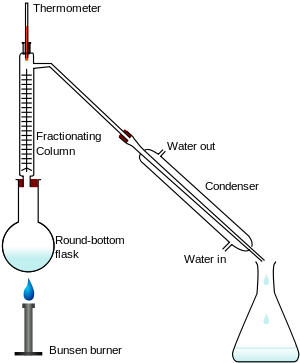
Fractional Distillation
Removes a liquid from a mixture of liquids, because liquids have different b.p.s
Mixture is heated to evaporate substance with lowest b.p.
some of the other liquid(s) will evaporate too.
A mixture of gases condense on the beads in the fractional column.
So the beads are heated to the boiling point of the lowest substance, so that substance being removed cannot condense on the beads.
The other substances continue to condense and will drip back into the flask.
Seperating Mixture of Two Solids
Can be done by dissolving one in an appropriate solvent. Then filter one and extract other from solution by evaporation. If one solid is magnetic, can use a magnet e.g. sand and iron fillings
| Solvent | It dissolves... |
|---|---|
| Water | Some salts, sugar |
| White spirit | Gloss paint |
| Propanone | Grease, nail polish |
| Ethanol | Glues, printing inks, scented substances |
Choosing a Suitable Method
| Method of separation | Used to separate |
|---|---|
| Filtration | A solid from a liquid |
| Evaporation | A solid from a solution |
| Crystallization | A solid from a solution |
| Simple Distillation | A solvent from a solution |
| Fractional Distillation | Liquids from each other |
| Chromatography | Different substances from a solution |