Air and Water
Tests for Water
| Test | Type of Test | Positive Result |
|---|---|---|
| Blue Cobalt(II) Chloride Paper | Chemical | Paper turns from blue to pink |
| Anhydrous Copper(II) Sulphate powder | Chemical | From white powder to blue crystals |
| Test m.p. and b.p. | Physical | m.p. at 0°C and b.p. at 100°C |
Purification of Water
Water is pumped into screens, which remove solid floating debris.
Aluminum sulfate is added to coagulate (stick together) small pieces of clay so that they are easily removed.
The water is then filtered through coarse sand to remove larger, insoluble debris.
The water encounters more flocculants (chemicals that make particles move down to bottom of tank) and is filtered again through fine sand.
Chlorine gas is bubbled through the water to kill bacteria. This makes the water slightly acidic, so to reverse this appropriate amounts of sodium hydroxide (an alkali) is added.
Some countries also add fluorine
Use of Water
| At Home | In Industry |
|---|---|
| Drinking | Dissolve |
| Cooking | Wash and cool things |
| Washing | In power stations where steam is used to turn turbines |
| On farms for animals & crops |
Air
Clean air is composed of approximately
79% nitrogen
20% oxygen
Remainder: noble gases, water vapor & carbon dioxide
Pollutants in Air
Pollutant | Source | Problems caused |
|---|---|---|
Carbon Monoxide CO | Incomplete combustion of carbon-containing substances | Reacts with haemoglobin, preventing it from carrying oxygen; death due to oxygen starvation |
Sulphur Dioxide SO2 | From combustion of fossil fuels which contain sulfur | Irritates eyes and throat, causes respiratory problems and causes acid rain |
Oxides of Nitrogen NOx | From car exhausts | Causes respiratory problems and forms acid rain |
Lead compounds | From burning of petrol as lead is added to it for better performance | Causes damage to brain and nerve cells in young children |
Fractional Distillation of Air
Air is filtered to remove dust
Water vapor and carbon dioxide removed, (because they would freeze and block the pipes):
air is cooled until water vapor condenses
then passes over absorbent beads to trap carbon dioxide
It is compressed, causing it to heat up. Cooled by recycling cold air
The cold compressed air is passed through a jet, into a larger space. It expands rapidly, making it very cold.
This is repeated, cooling the air more. By -200°C it is liquid except for neon and helium. These gases are removed. They can be separated from each other by absorption on charcoal.
The liquid air is pumped into the fractioning column. There it is slowly warmed up. The gases boil off one by one, and are collected in tanks or cylinders.
Sources of methane: oil and natural gas, decomposition of vegetation, and waste gases from digestion in animals
Catalytic Convertor
In the combustion engine, insufficient amounts of oxygen lead to incomplete combustion of the carbon containing fuel
Gases produced: (a) carbon monoxide (b) oxides of nitrogen
A catalytic convertor catalyzes the reduction of NO~2~ to nitrogen gas N~2~ and catalyzes the oxidation of CO to CO~2~
Rust Preventition
Coating with something to prevent contact with air and moisture
Plastic, paint and grease
Electroplating with tin or chromium
Galvanising: dipping in molten zinc
Sacrificial protection: attaching a piece of metal that is more reactive that iron to object, commonly magnesium or zinc. This will corrode in the place of iron.
Fertilizer
NPK used in fertilizers because:
Nitrogen is needed for chlorophyll and other proteins.
Phosphorus helps roots grow and crops ripen.
Potassium helps make proteins and resist diseases.
All alkalis (except ammonia) will react with ammonium compounds, removing ammonia, for example:
Calcium hydroxide+Ammonium chloride→Calcium Chloride+Water+Ammonia
Greenhouse Gases
The greenhouse gases are: carbon dioxide and methane.
They stop heat escaping in to space.
Too much greenhouse gases leads to climate change.
This will cause the ice poles to melt, rising sea levels, more droughts, storms, floods and famine; global warming
Formation of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is produced whenever carbon or any of its compound are completely burned in excess oxygen
It is also formed as a product of respiration
It is produced as product of reaction between an acid and carbon
From the thermal decomposition of a carbonate
Haber Process
- Industrial manufacture of ammonia NH~3~
N~2~ (g) + 3H~2~ (g) ⇌⇌ 2NH~3~ (g)
Raw materials:
Nitrogen: from the air
Hydrogen: methane + steam → carbon dioxide + hydrogen
Essential conditions:
Temperature: 450°C
Pressure: 200atm
Catalyst: Iron
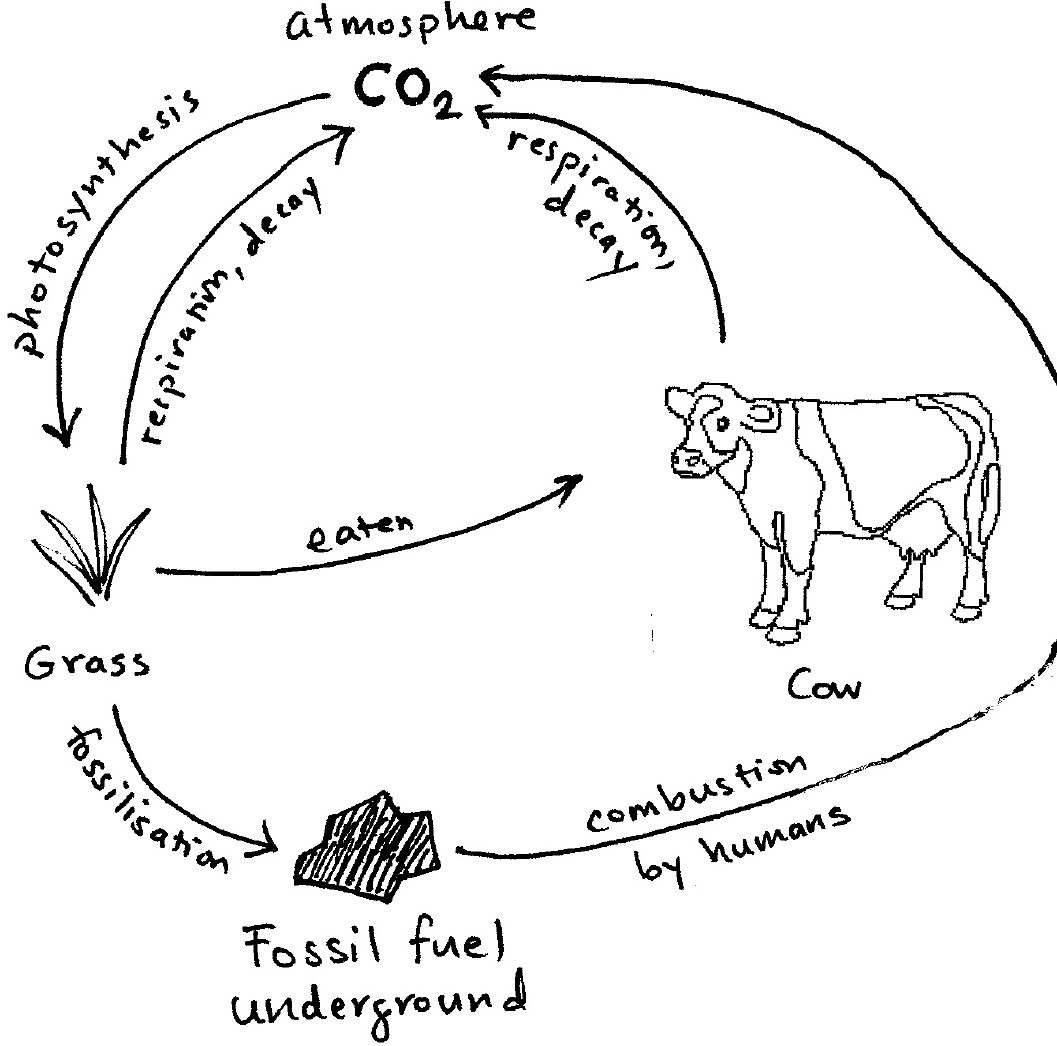
Carbon Cycle